Michael Gaudreau
Staples Team Supervisor/Software Engineering Graduate of @flatiron-school
The Big O
Published May 04, 2020
Understanding Big O notation is essential part of becoming a good programmer, it allows you gauge the difference between algorithms in terms of efficiency. It specifically describes the worst-case scenario of a algorithm and can be looked at in terms of space or time and is composed these different complexities. We will take a look at the first 4 of these notations in this post.
- O(1)
- O(n)
- O(n²)
- O(log n)
- O(n log n)
- O(2^n)
- O(n!)
Don’t worry if that seems totally alien to you at this point, it will make more sense by the end of this post!

O(1) - Constant Runtime
This is the most optimal case where the complexity stays constant no matter how the input differs. An example of this would be a function such as the following.
function firstElement(array){
return array[0];
}
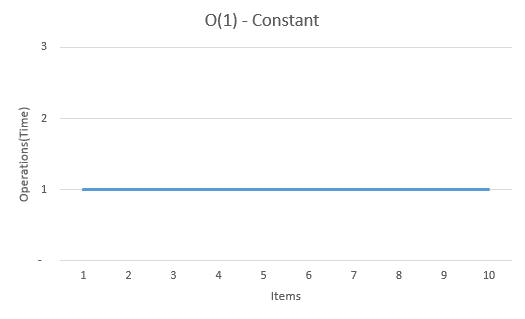
With this function it doesn’t matter how big the array passed in a as a argument is, whether it have a size of 10 elements or 1000 elements it should always take the same amount of time and space to run. A real world analogy would be inspecting the cover of a book, because the cover is always going to be first thing you see when passed a book, no matter if the book is 25 pages or 500 pages long it should always take the same amount of time to look at the front cover.
O(n) — Linear
Linear notation is where the complexity grows as the size of the input grows, meaning the larger and more complex the input given, the more time/space that is required for the process. This shows a simple example in code.
function alertArray(array){
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
alert(array[i]);
}
}
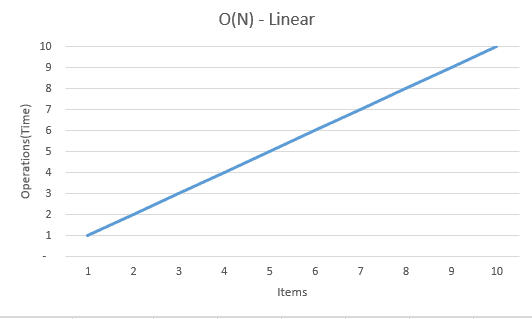
So here when we pass in a array of size 10 vs a array of size 100 the complexity of the algorithm is multiplied by 10. Simple the more data passed in the longer the process and more space required to complete it. Using the same inputs as the previous real world example where we have a book with 25 pages and book with 500 pages its going take you 20 times longer to read through the whole larger book than the smaller one.
O(n²) — Quadratic
Loops in your code are costly in terms of time and space and when you have nested loops in your code it’s going to increase the complexity in a quadratic manner. A simple code example for quadratic notation would be.
function containsDuplicate(array){
for (const elem1 of array){
for (const elem2 of array){
if (elem1 === elem2){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
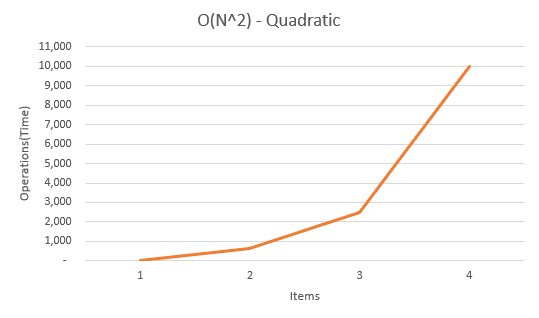
This algorithm is going to loop through all the elements of a array for every single element making the complexity grow exponentially as the size of the array passed in as input gets larger.
O(log n) — Logarithmic
Essentially logarithmic complexity is the opposite of a an exponential function or the opposite of a O(n2) notation. This means that the larger the input is the smaller the proportion of the actual input needs to be processed.
function f(n) {
let i;
for (i = 1; i < n; i=i*2){
console.log(i);
}
}
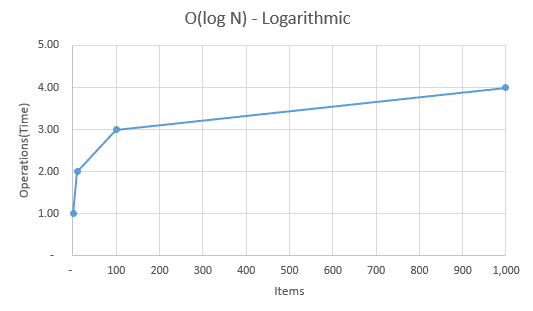
A real world example of this would be finding a specific page in a large book by splitting it in two, until you are at the page your looking for. So if you had a 200 page book and needed page 175 you split the book about in the middle say page 98, then again split the part that is page 98-200 in two again, at say page 146 then continue this pattern until you are at the correct page.
Conclusion
These are a few simple examples of algorithms and the corresponding Big O notation to help you get a basic understanding of what each one means. It is by far not the most in depth explanation and I urge you to do your own research to really get a good handle on the different types and how to implement them. You take a look at this page from interviewcake.com that has a good explanation of the the same concepts.